Strength of Material
Mechanical Properties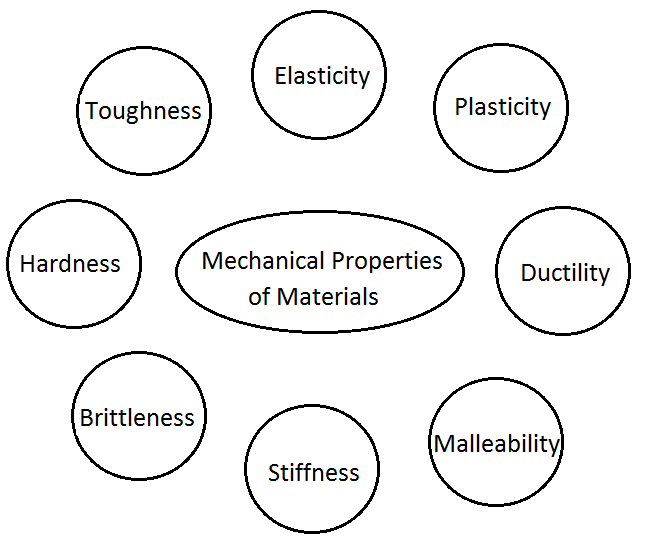
- Hardness ;Resist the penetration (impact load)
- Strength : Ability of material withstand of material without failure.
- Elasticity : It regain the original shape after removing load
- Plasticity : Permanent deformation after removing load.
- Mali ability : Converts to thin sheet without rupture
- Ductility : Draw in to thin wire.
- Brittleness : No deformation takes place & rupture (lake of ductility ) (cast iron)
- Toughness : absorb energy & plastic deformation without rupture.
- Fatigue: by repeatedly applied load program me and localized structure damage that occur.
- Creep : tendency of solid material to move slowly deform permanently under mechanical stress.

Stress : Load applied on particular area.
- it is tensor quantity
- unit : N/mm2
- it has no unit.
Strength of Material
Tensile : when body is subjected to equal and opposite pull.Compressive : when body is subjected to equal and opposite push.
Thermal stress : stress due to change in temperature.
Linear strain : deformation of bar per unit length in direction of force.
Lateral strain : Direct stress dis accomplished strain in its own direction & opposite kind of strain in every direction at right angle is known.
Poison 's ration = Lateral strain / Linear strain
- it has no unit
- max poison ratio = 0.5 (rubber)
E = 9KC /(3K+C)
Principle stress & strain:
- 3 planes are mutually perpendicular to each other
- Carries direct stress only
- No shear stress
- 3 direct stress (Max, min, intermediate)
Resilience: Strain energy stored in body due to external loading with in the elastic limit.
Bending Assumption :
- Material is homogeneous.
- obey hook's law.
- Transverse section plane before and after bending.
- Each layer is free to explained.
- Value of young s modulus is same in tension and compression.
Strength of Material
Bending equation:(M/I)=(SIGMA /Y)=(E/R),
M= Bending Moment
I = Moment of inertia
Y = Distance from center
E = Young 's modulus
R = radius of curvature
Shear stress in shaft
(Tou/R) = (T/J) = (C x thita )/l
Tou = Shear stress
R = Radius of shaft
T = torque
J = polar moment
C = Rigidity
thita = angle of twist
l = length of shaft
Stiffness of spring : load required to produce unit deflection in spring is called stiffness of spring.
vipul baria
Comments
Post a Comment